Wall Street saw stocks end October with a whimper, although equities began November on a high note. Each of the benchmark indexes listed here closed last week lower, except the Russell 2000. A surprisingly weak jobs report (see below) at the end of the week was offset by solid earnings reports from a couple of tech giants. Analysts speculated that the October labor data was impacted by hurricane disruptions and a strike at a major airplane manufacturer. Consumer discretionary and communication services were the only market sectors to end the week higher. Utilities, real estate, and information technology fell the furthest. Ten-year Treasury yields reached the highest rate in nearly four months as the latest economic data favored a slightly more hawkish Federal Reserve. Crude oil prices closed the week with three consecutive days of gains, but not enough to recover from a downturn earlier in the week.
Stocks ended higher last Monday as investors awaited a batch of major corporate earnings reports. The Russell 2000 added 1.6% to lead the benchmark indexes listed here. The Dow advanced 0.7%, followed by the Global Dow, which rose 0.5%. The NASDAQ and the S&P 500 each gained 0.3%. Ten-year Treasury yields closed at 4.27%, an increase of 4.6 basis points. Crude oil prices plunged 5.2% to $68.02 per barrel after Iranian crude oil facilities escaped Israeli bombardment, easing fears of disruptions to energy supplies. Both the dollar and gold prices were relatively unchanged by the close of trading.
Last Tuesday saw the NASDAQ (0.8%) and the S&P 500 (0.2%) close higher, while the remaining indexes ended the session in the red. The Dow fell 0.4%, while the Russell 2000 and the Global Dow each ended the day down 0.3%. Yields on 10-year Treasuries remained at 4.27%. Crude oil prices slid to $67.30 per barrel. The dollar was flat, while gold prices rose 1.1%.
Investors were cautious last Wednesday ahead of earnings results from some big tech companies. Each of the benchmark indexes listed here lost ground, led by the NASDAQ (-0.6%), and followed by the Global Dow (-0.5%), the S&P 500 (-0.3%), the Dow (-0.2%), and the Russell 2000 (-0.2%). Ten-year Treasury yields ticked lower, settling at 4.26%. Crude oil prices rebounded, gaining 2.5% to close at about $68.91 per barrel. The dollar fell 0.2%, while gold prices rose 0.6%.
Stocks continued to trend lower last Thursday as weak earnings data from some tech giants dampened investors’ zeal for risk. The NASDAQ fell 2.8%, followed by the S&P 500 (-1.9%), the Russell 2000 (-1.6%), the Dow (-0.9%), and the Global Dow (-0.8%). Crude oil prices climbed higher for the second straight day, gaining 2.8% to close at $70.62 per barrel. Ten-year Treasury yields inched up 1.8 basis points to 4.28%. The dollar and gold prices declined.
Wall Street kicked off November with a bang as stocks closed sharply higher last Friday. Strong earnings from two giant tech companies bolstered market sentiment despite a weak jobs report. The NASDAQ (0.8%) led the benchmark indexes listed here, followed by the Dow (0.7%), the Russell 2000 (0.6%), the S&P 500 (0.4%), and the Global Dow (0.3%). As stocks moved higher, bond values declined, pushing yields higher. Ten-year Treasury yields ended the session up 1.8% to close at 4.36%. Crude oil prices rose 0.4%. Gold prices dipped 0.2%, while the dollar gained 0.4%.
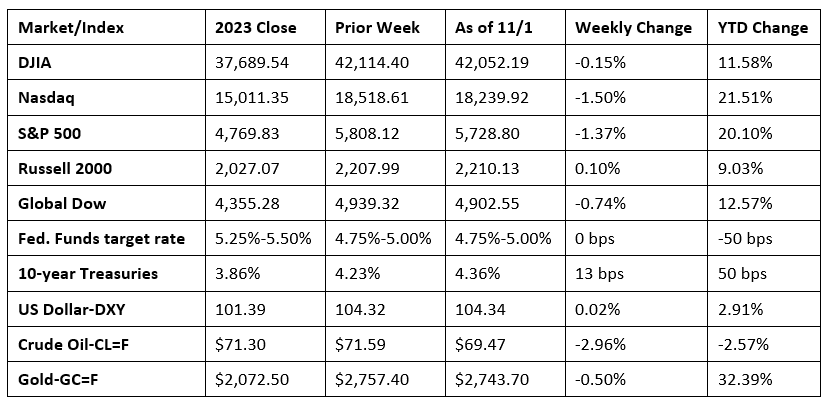
Chart reflects price changes, not total return. Because it does not include dividends or splits, it should not be used to benchmark performance of specific investments.
Last Week’s Economic News
- Employment was essentially unchanged (+12,000) in October after adding 223,000 (revised) new jobs in September. The average monthly gain over the prior 12 months was 194,000. According to the latest report from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, Hurricanes Helene and Milton may have impacted the collection and accuracy of data in October. Nevertheless, the unemployment rate remained at 4.1%, while the number of unemployed persons increased by 150,000. These measures are higher than a year earlier, when the jobless rate was 3.8%, and the number of unemployed people was 6.4 million. The labor force participation rate fell 0.1 percentage point to 62.6%. The employment-population ratio declined 0.2 percentage point to 60.0%. The number of long-term unemployed (those jobless for 27 weeks or more) was little changed at 1.6 million in October. This measure is up from 1.3 million a year earlier. In October, the long-term unemployed accounted for 22.9% of all unemployed people. The change in total employment for August was revised down by 81,000, and the change for September was revised down by 31,000. With these revisions, employment in August and September combined was 112,000 lower than previously reported. In October, average hourly earnings rose by $0.13, or 0.4%, to $35.46. Over the past 12 months, average hourly earnings have increased by 4.0%. The average workweek was unchanged at 34.3 hours in October.
- According to the initial estimate, third-quarter gross domestic product increased at an annual rate of 2.8%. In the second quarter, GDP advanced 3.0%. The increase in GDP primarily reflected increases in consumer spending (3.7%), exports (8.9%), and federal government spending (9.7%). Imports, which are a subtraction in the calculation of GDP, increased 11.2%. The personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index increased 1.5%, compared to an increase of 2.5% in the second quarter. Excluding food and energy prices, the PCE price index increased 2.2% (2.8% in the second quarter).
- In September, personal income and disposable personal income each increased 0.3%. Personal consumption expenditures (PCE) advanced 0.5%. The PCE price index moved up 0.2%. Excluding food and energy (core prices), the PCE price index rose 0.3%. Over the last 12 months, the PCE price index climbed 2.1%, while the core PCE price index increased 2.7%.
- The international trade in goods deficit increased $14.0 billion, or 14.9%, in September over the prior month. A $10.4 billion increase in imports more than offset a $3.6 billion decrease in exports.
- According to the latest Job Openings and Labor Turnover Summary, the number of job openings in September, at 7.4 million, declined about 400,000 from the August estimate and decreased 1.9 million since September 2023. The number of hires changed little at 5.6 million in September. The number of total separations in September was unchanged at 5.2 million but was down 326,000 over the last 12 months. In September, the number of quits changed little at 3.1 million but declined 525,000 over the year. The number of job openings for August was revised down by 179,000 to 7.9 million, the number of hires was revised up by 118,000 to 5.4 million, and the number of total separations was revised up by 171,000 to 5.2 million.
- New orders continued to decline in the manufacturing sector, according to the latest survey results from the S&P Global US Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index™ (PMI®). On the plus side, the pace of the decline was the slowest in three months. Nevertheless, manufacturers continued to reduce employment and purchasing activity. The October PMI was 48.5, up from 47.3 in September, but below the 50.0 no-change mark for the fourth consecutive month.
- The national average retail price for regular gasoline was $3.097 per gallon on October 28, $0.047 per gallon below the prior week’s price and $0.376 per gallon less than a year ago. Also, as of October 28, the East Coast price declined $0.009 to $3.045 per gallon; the Midwest price decreased $0.083 to $2.923 per gallon; the Gulf Coast price inched down $0.074 to $2.646 per gallon; the Rocky Mountain price dipped $0.023 to $3.198 per gallon; and the West Coast price fell $0.061 to $3.973 per gallon.
- For the week ended October 26, there were 216,000 new claims for unemployment insurance, a decrease of 12,000 from the previous week’s level, which was revised up by 1,000. According to the Department of Labor, the advance rate for insured unemployment claims for the week ended October 19 was 1.2%, unchanged from the previous week’s rate, which was revised down by 0.1 percentage point to 1.2%. The advance number of those receiving unemployment insurance benefits during the week ended October 19 was 1,862,000, a decrease of 26,000 from the previous week’s level, which was revised down by 9,000. States and territories with the highest insured unemployment rates for the week ended October 12 were New Jersey (2.1%), California (1.9%), Puerto Rico (1.8%), Washington (1.8%), Nevada (1.6%), Rhode Island (1.6%), Illinois (1.4%), Massachusetts (1.4%), Michigan (1.4%), and New York (1.4%). The largest increases in initial claims for unemployment insurance for the week ended October 19 were in Florida (+4,501), Kansas (+304), Wisconsin (+222), Hawaii (+103), and Idaho (+101), while the largest decreases were in New York (-2,785), North Carolina (-2,767), California (-2,012), Texas (-1,865), and Georgia (-1,852).
Eye on the Week Ahead
The first full week of November is somewhat lacking in the release of important economic data. However, the focus will be on the Federal Reserve’s statement following its latest meeting on November 7. After reducing the federal funds target range by 50.0 basis points in September, it is possible that the Fed will make no changes in November and may wait until its final meeting of the year in December to adjust rates further.
The Week Ahead

The information provided is obtained from sources believed to be reliable. Forecasts cannot be guaranteed. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results.
© 2021 Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. All Rights Reserved.